The ASIL Level (Automotive Safety Integrity Levels) is related to the prevention or mitigation of the associated hazards in order to avoid unreasonable risk in using any automotive systems.
ASIL Level vs. HARA method
The ASIL Level is calculated with the HARA method, which aims at identifying and categorizing hazardous events of items, and also at specifying safety goals according to ISO 26262.
HARA (Hazard and Risk Assessment Analysis) is assessed in the early stages of the Safety Lifecycle, so it takes place after item definition to address safety goals and various design and performance requirements for the automotive systems.
This means that the combination of a hazard and an operational situation is considered as a hazardous event, that’s why the hazard and risk analysis must be carried out in the concept phase, i.e. in the early stages of an item’s lifecycle.
Therefore, the scope of the HARA analysis for identifying the Automotive Safety Integrity Level is:
- To identify and classify hazardous events caused by the item’s malfunctioning behaviour
- To formulate safety objectives with their corresponding ASILs related to the prevention or mitigation of hazardous events, in order to avoid unreasonable risks
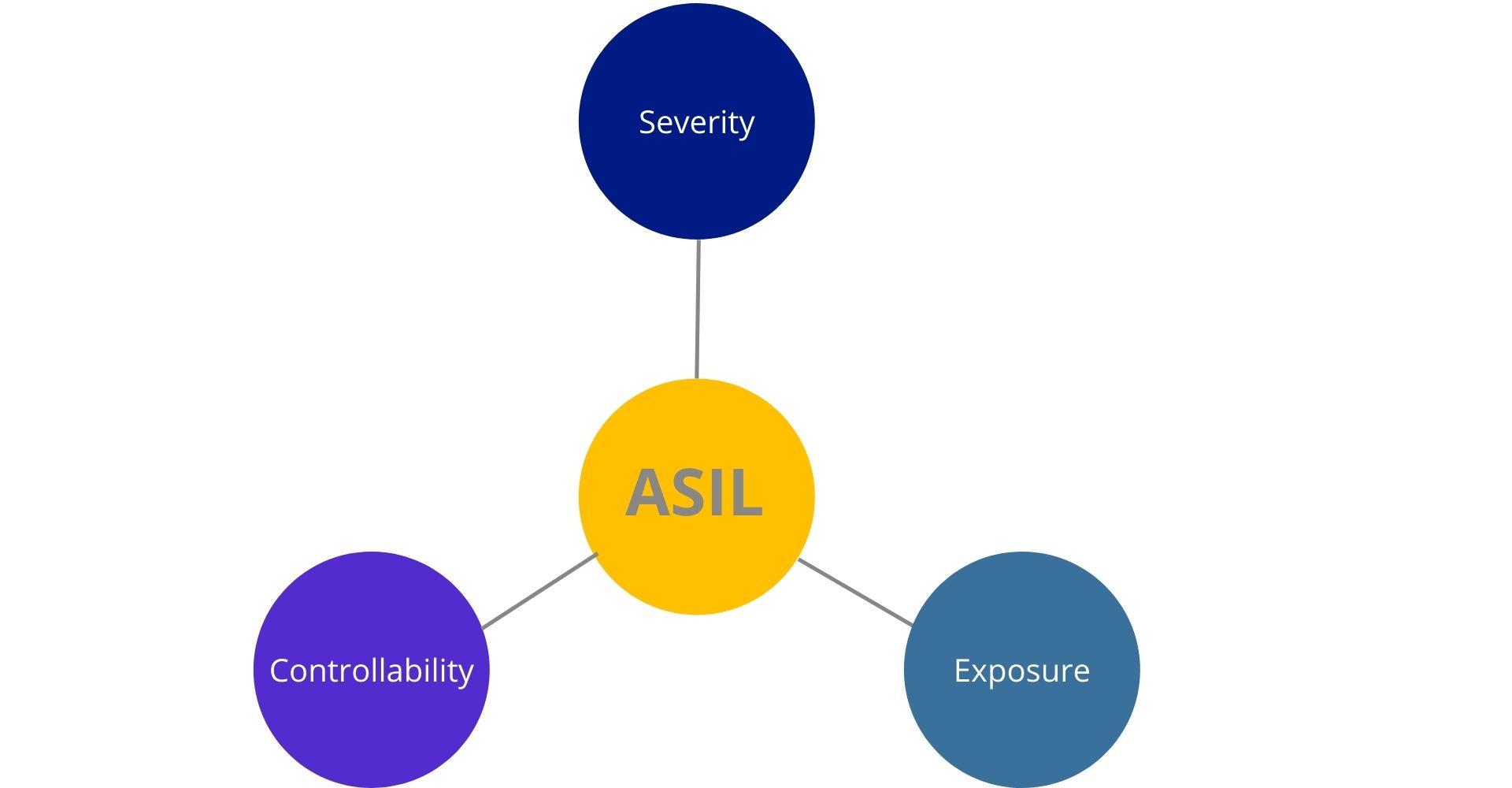
The ASIL Level is determined by considering:
- Severity
- Probability of exposure
- Controllability
In sum, the operational situations and modes of operation in which the incorrect behaviour of an item will result in a hazardous event shall be described by the HARA analysis, both when the vehicle is used correctly and when it is used incorrectly and reasonably foreseeable.
ASIL Classification by using HARA
As mentioned, ASIL is determined by considering three different parameters:
1) Severity
Severity is the estimate of the extent of harm to one or more individuals that can occur in a potentially hazardous event, such as damages to the driver, passengers, others outside the vehicle (based on Annex B ISO 26262-3). When the class of severity is S0, ASIL is not required.
2) Probability of Exposure
It is the state of being in an operational situation that can be hazardous if coincident with the failure mode under analysis (based on Annex B ISO 26262-3). The probability of exposure can be seen in terms of frequency of exposure or duration of exposure. Still, E0 does not require the ASIL assignment.
3) Controllability
Controllability is the ability to avoid a specified harm or damage through the timely reactions of the persons involved, possibly with support from external measures (based on Annex B ISO 26262-3). Reasonably foreseeable improper actions (e.g. failure to keep a safe distance) should be taken into account when analysing controllability parameter. The C0 does not require to determine the ASIL.
The ASIL classification using the HARA method provides with a view of hazardous events that may have safety consequences and safety requirements.
The QM (Quality Management) classification, instead, indicates that the quality processes are sufficient to manage the identified risk.
Do you need immediate assistance in regard to ISO 26262?
Go back to the blog
